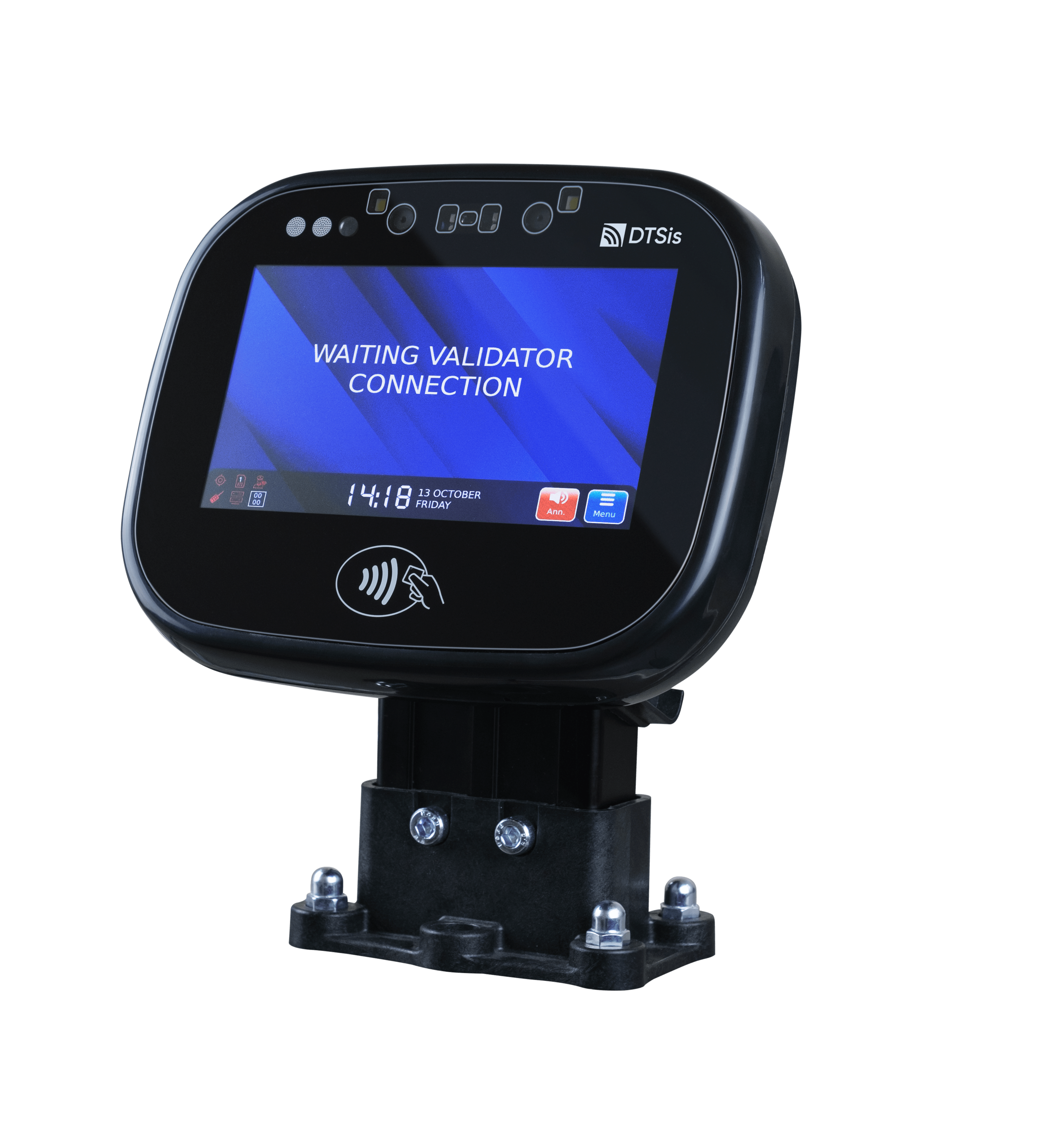
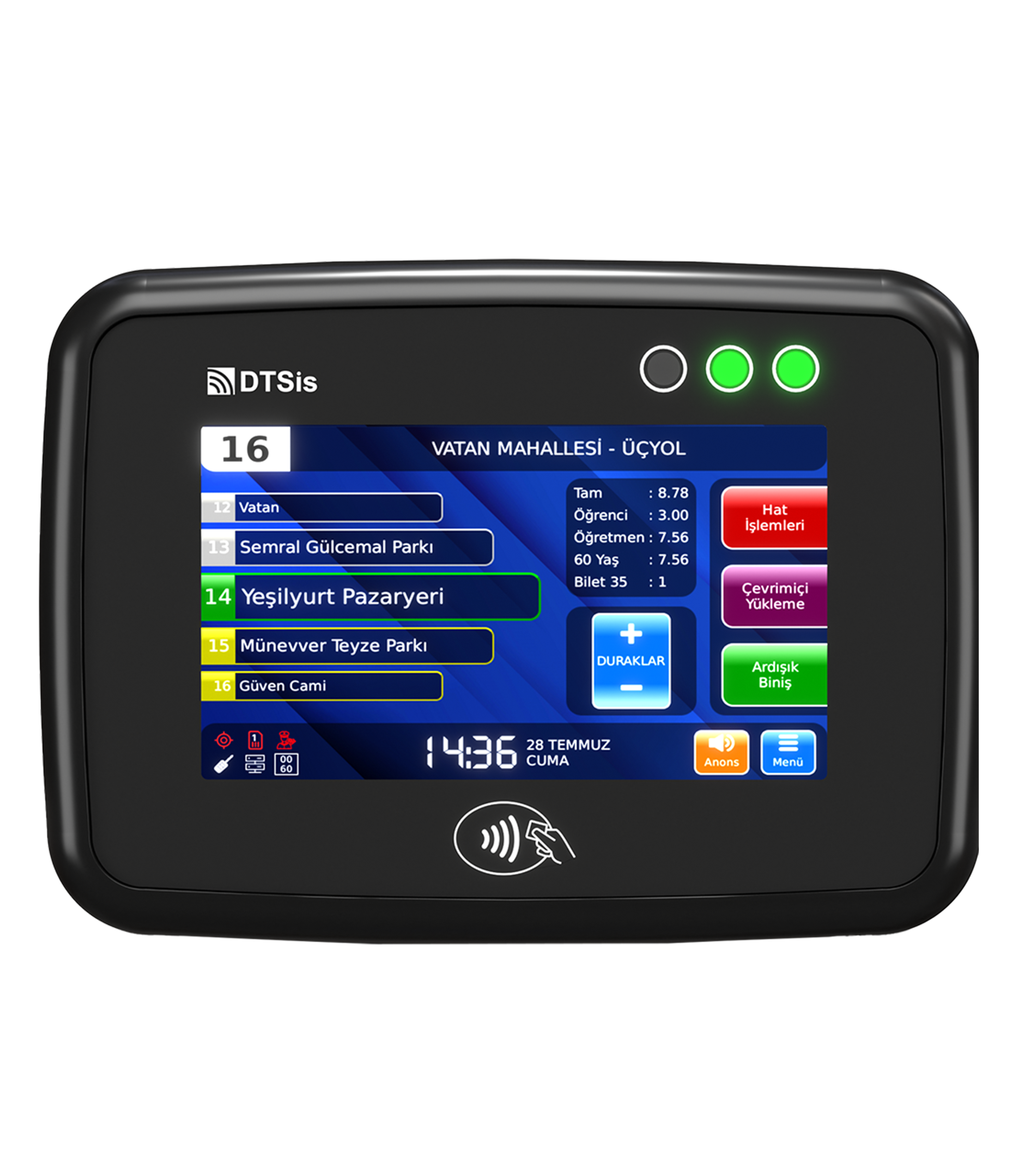
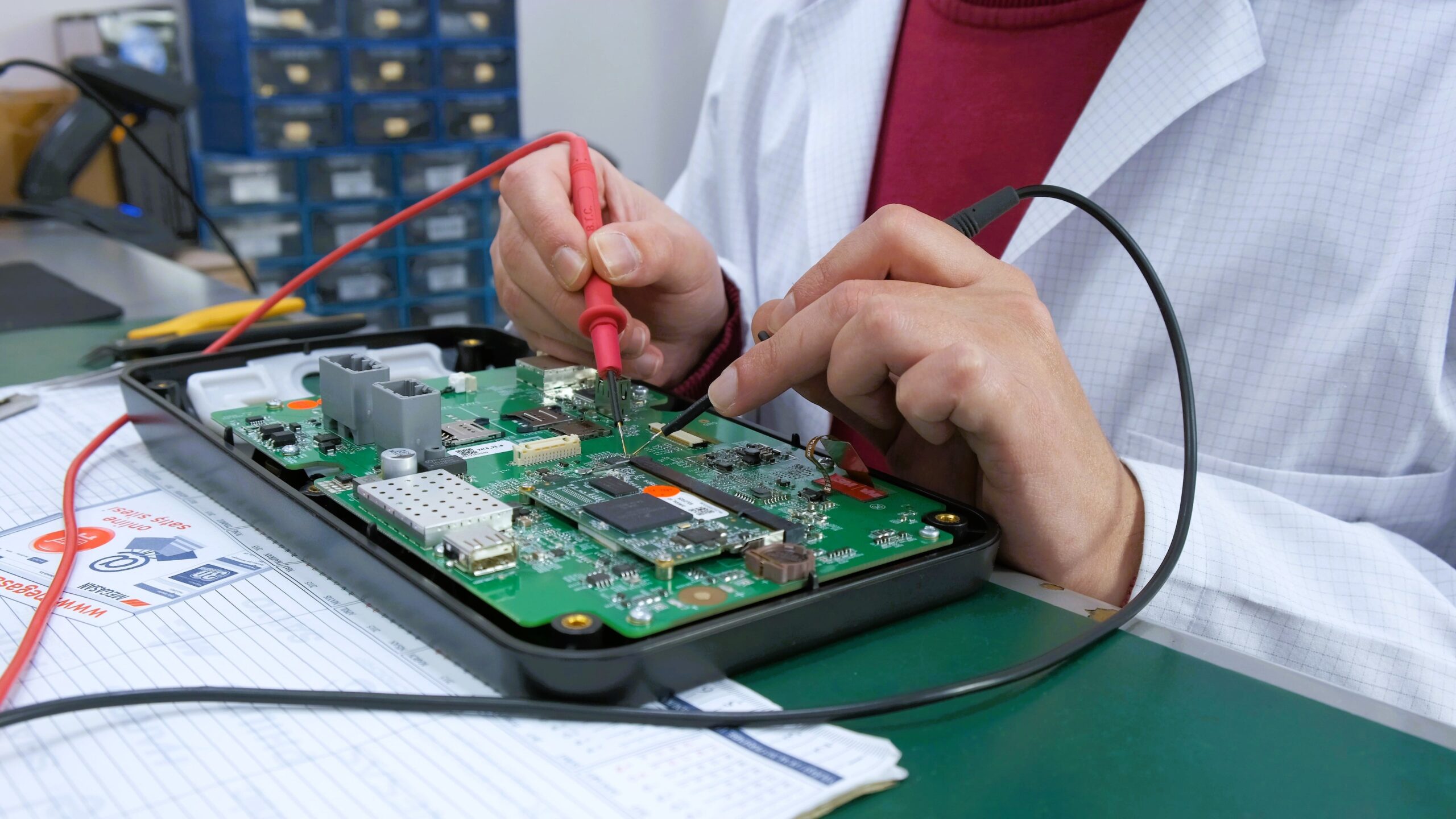
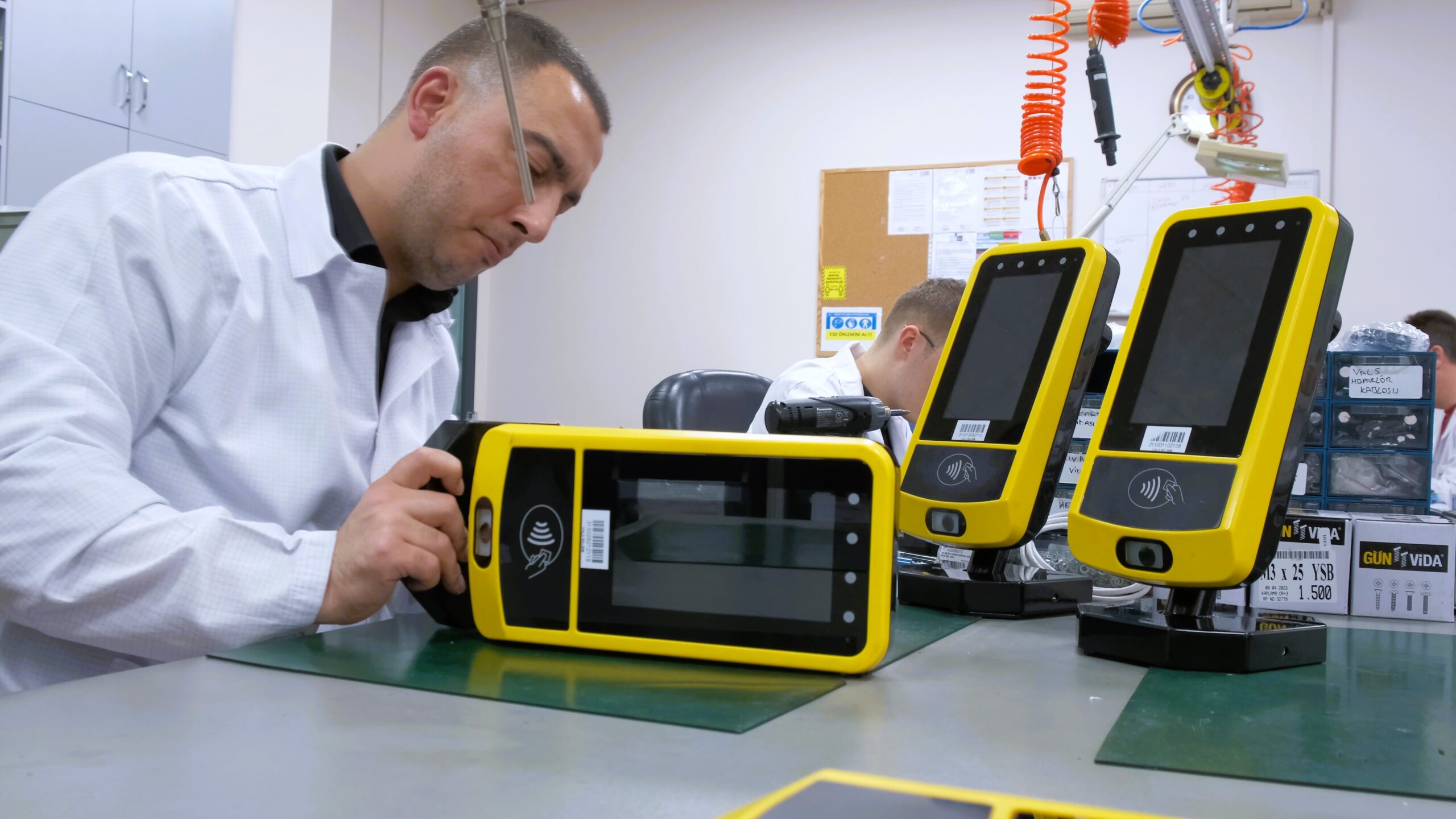
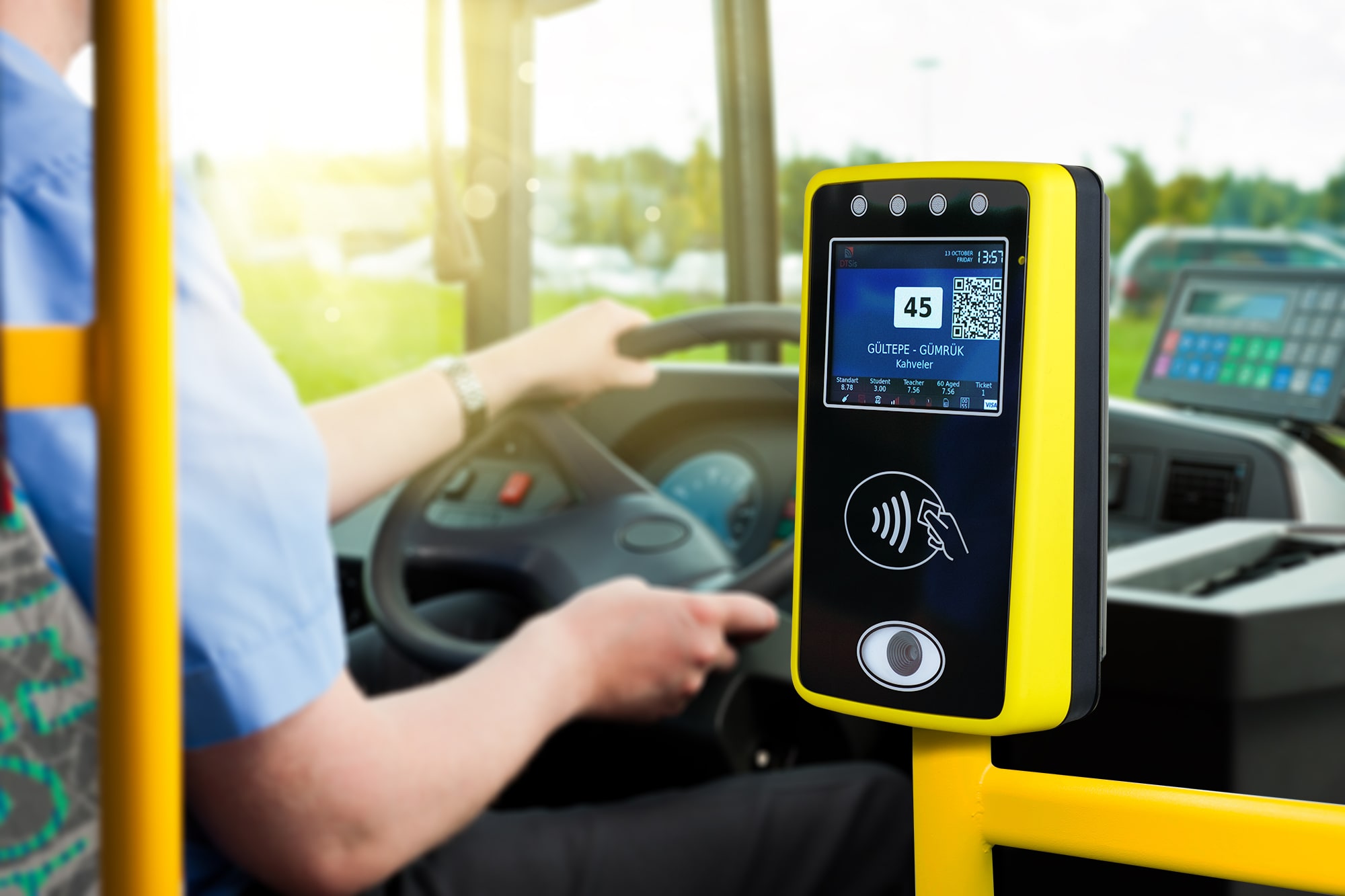
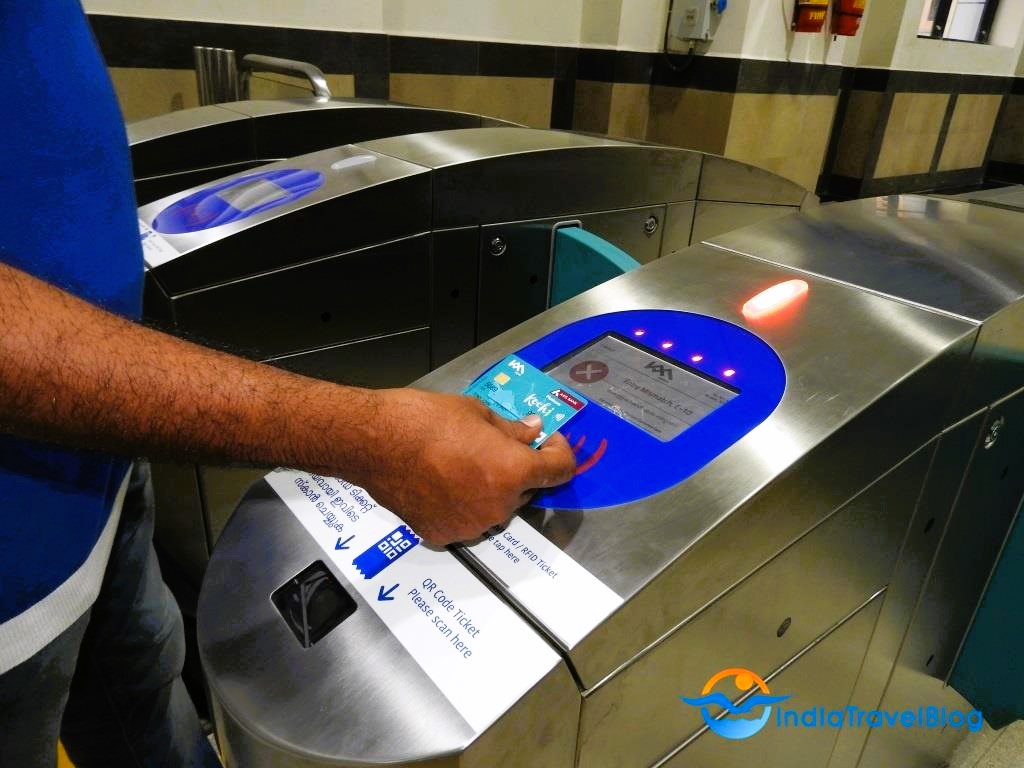
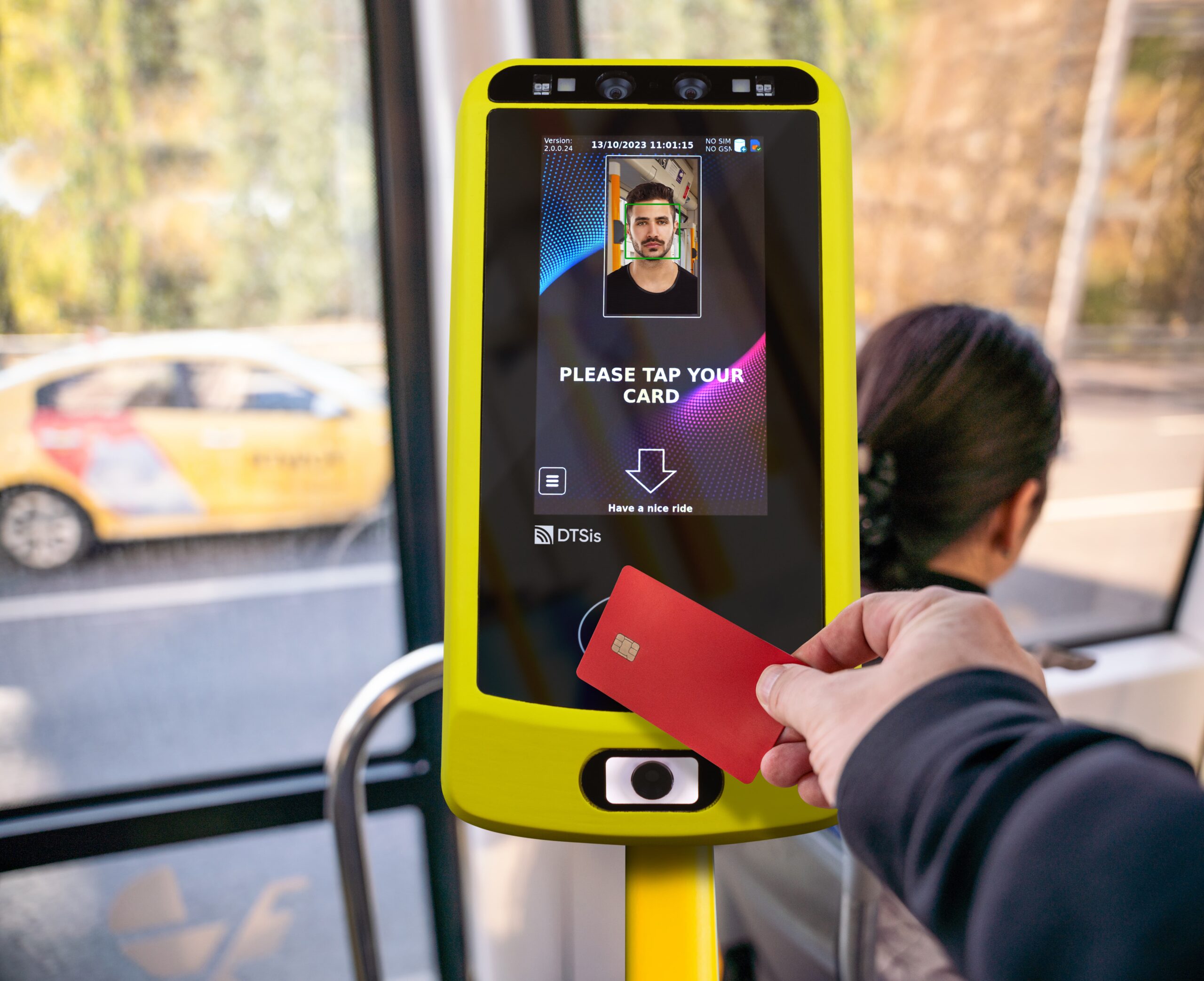
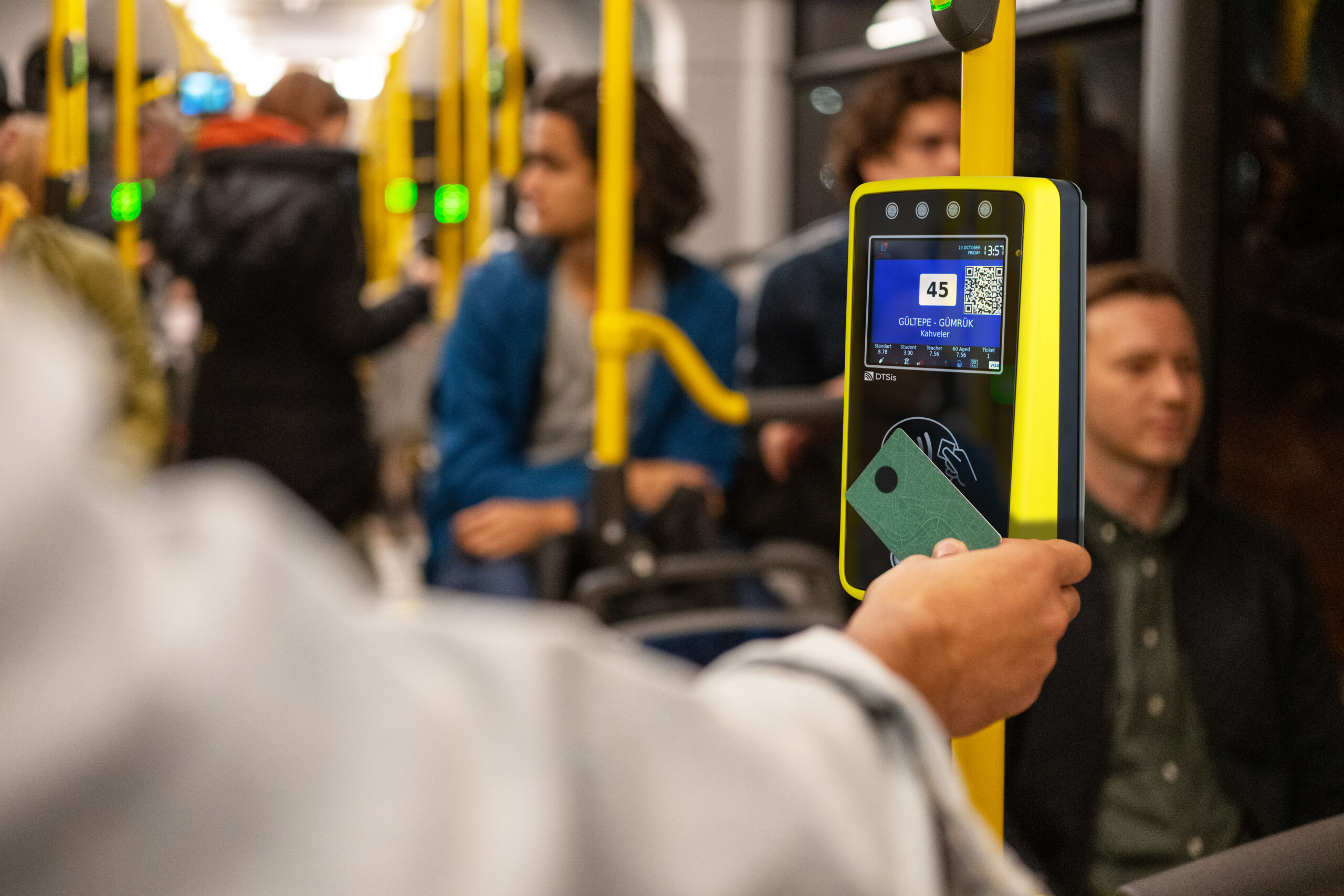
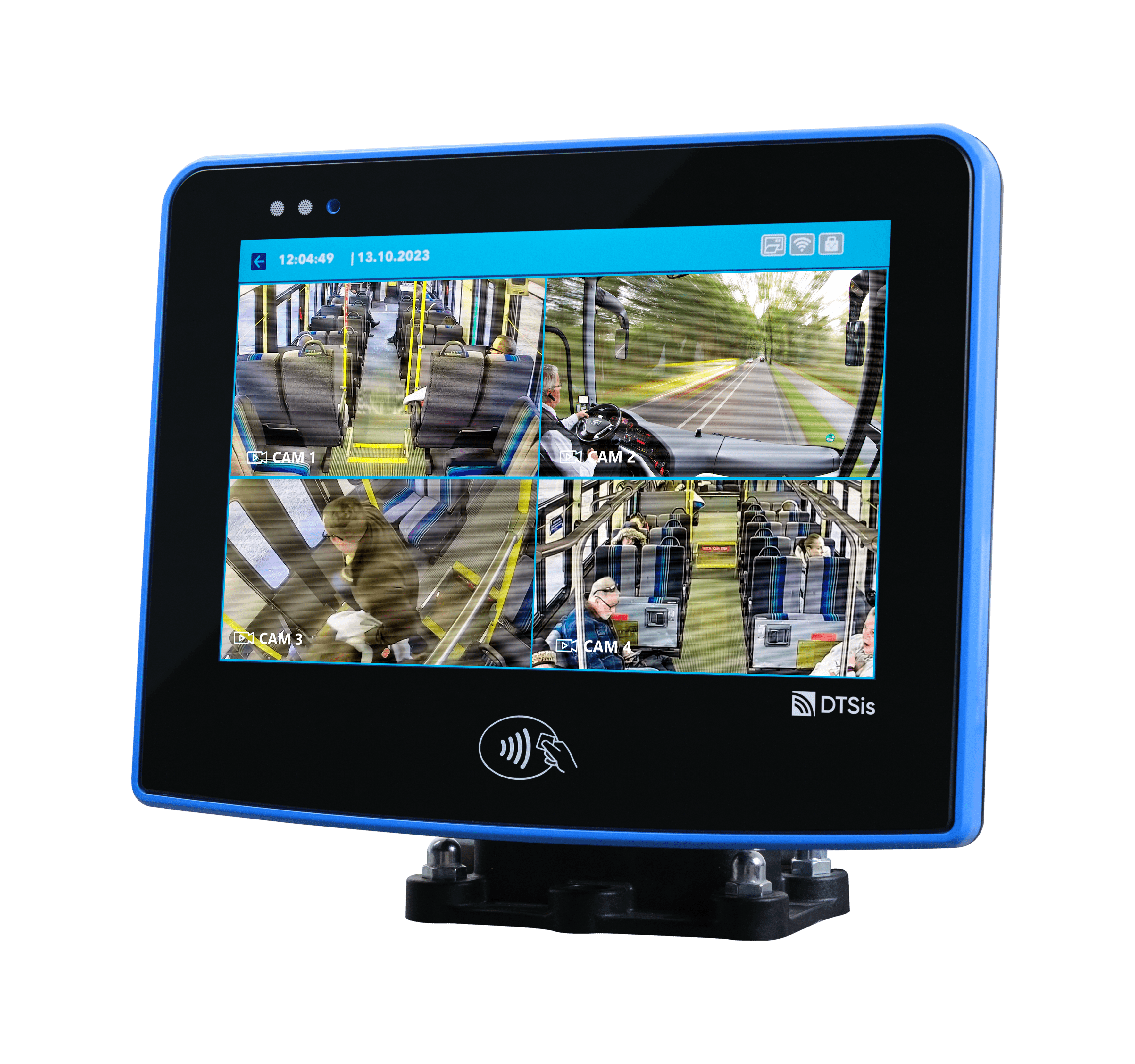
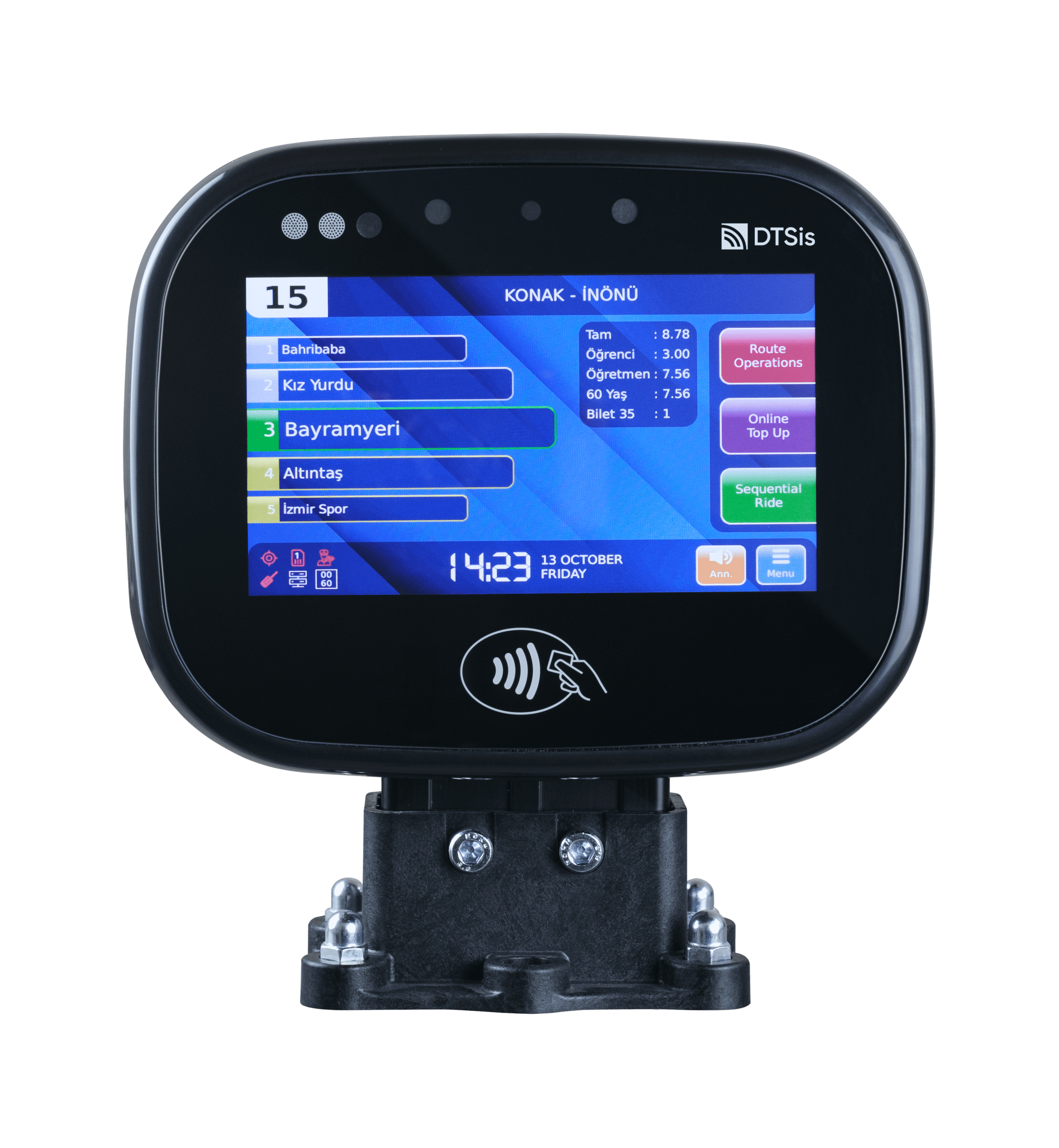
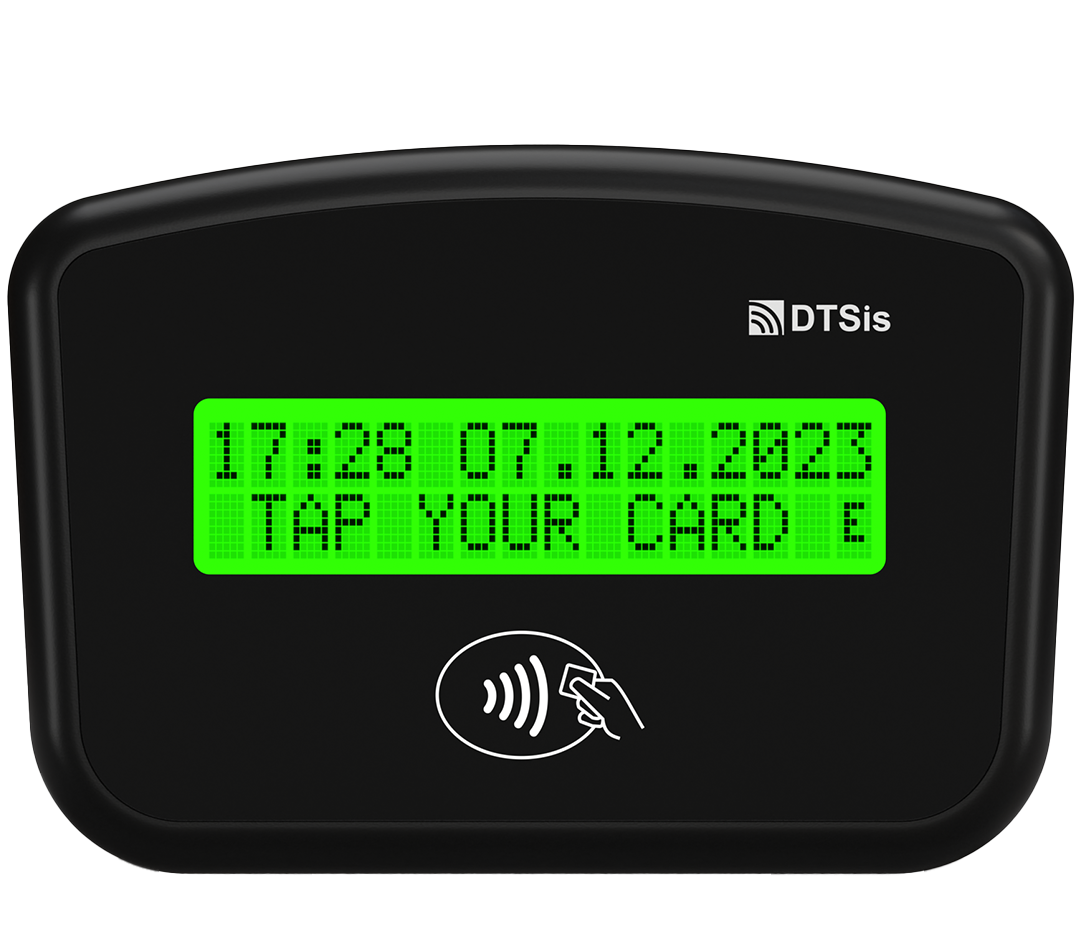
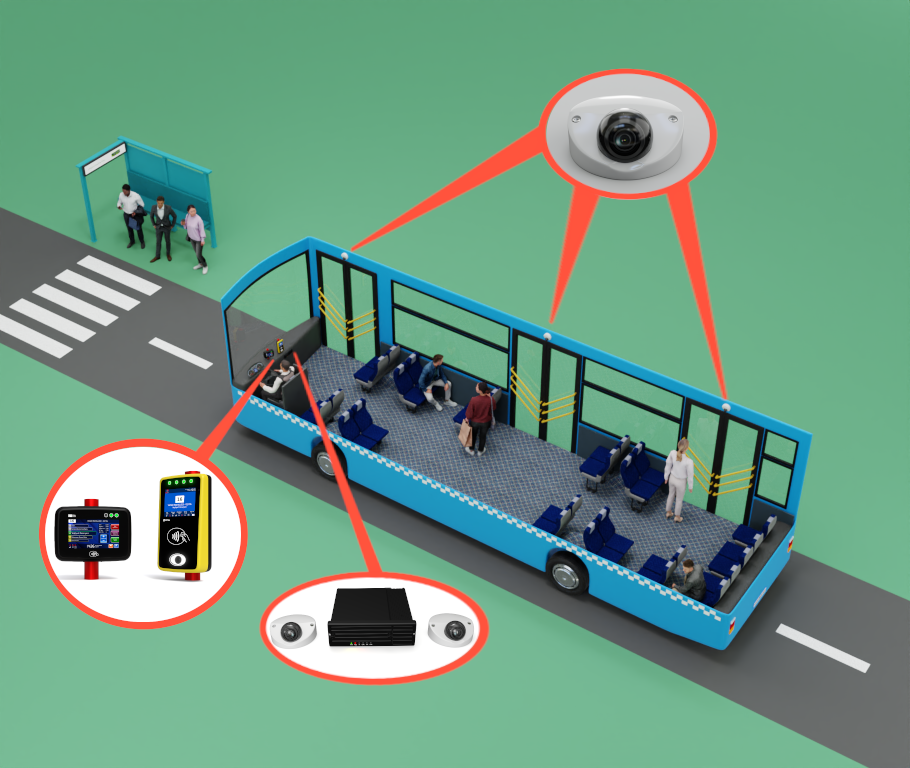
In the fast-paced digital world we live in today, technology continues to revolutionize various aspects of our daily lives. One area where technology has made a significant impact is in the realm of smart ticketing systems. Embedded Systems for Smart Ticketing are specialized computing systems designed to handle and process ticketing transactions within transportation and other services. These systems integrate hardware and software to provide efficient, secure, and user-friendly ticketing solutions. Embedded systems in smart ticketing provide numerous benefits, enhancing both user experience and operational efficiency.
According to Statista, the global market for smart ticketing is projected to reach $47.5 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.4% from 2020. This highlights the growing demand for innovative, efficient, and secure ticketing solutions.
Embedded systems are particularly well-suited for this expansion due to their low power consumption and compact size—two key factors that allow them to perform consistently over time in mobile devices, fare collection systems, and transport infrastructure. A study by MarketsandMarkets estimates that the global embedded systems market is expected to grow from $90.2 billion in 2020 to $130.1 billion by 2025, reinforcing their central role in next-generation technologies like smart ticketing.
Key advantages for Users:
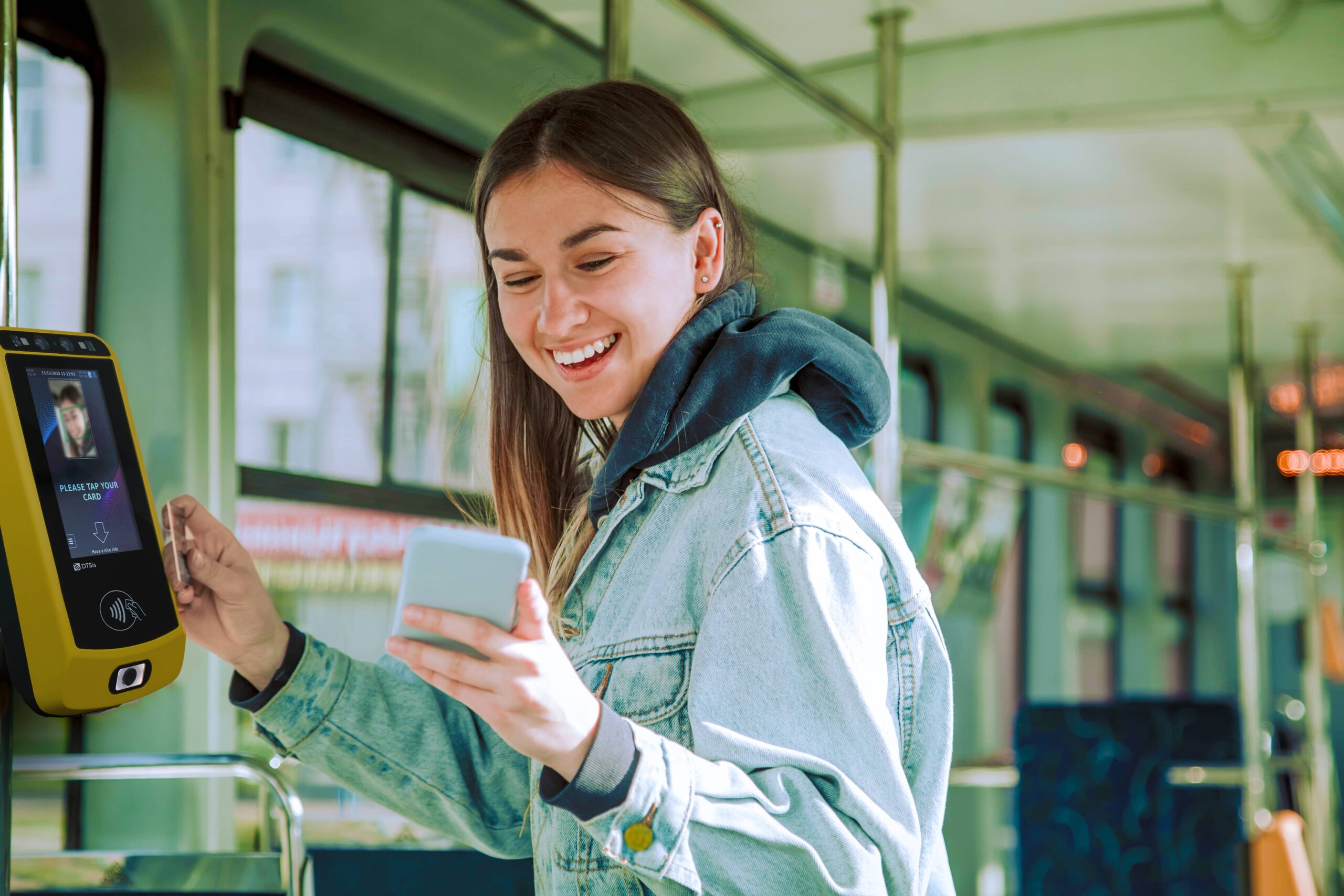
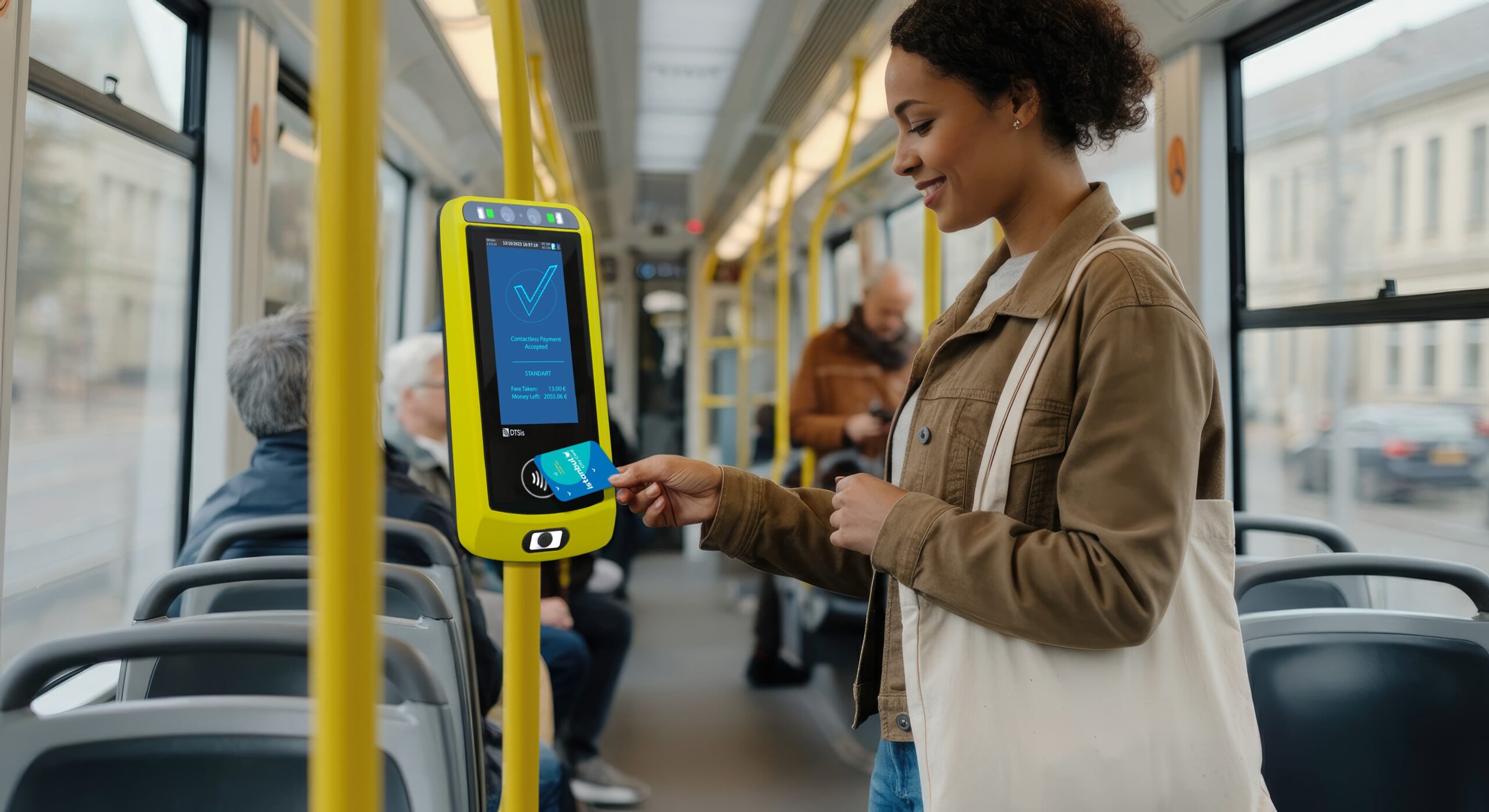
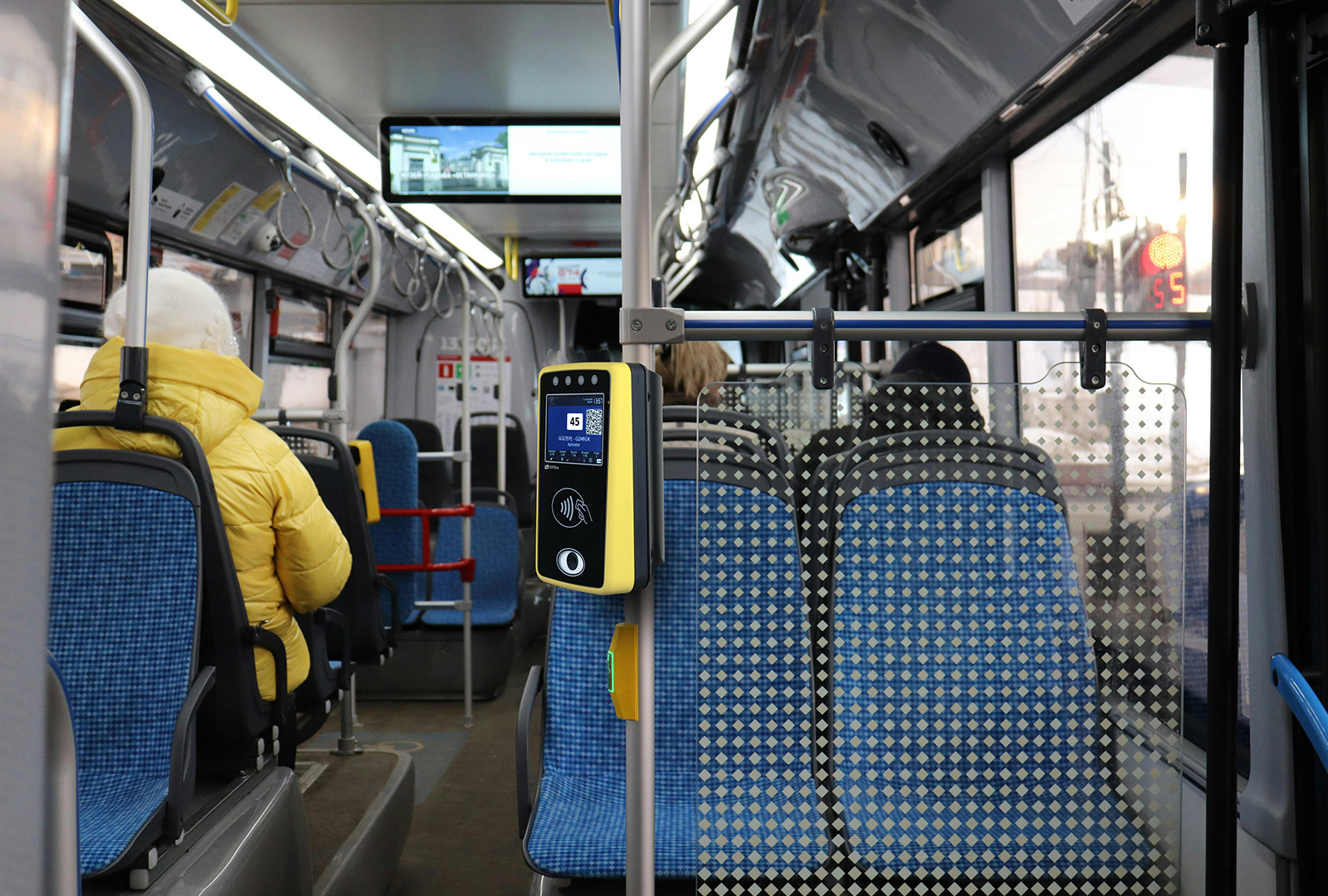
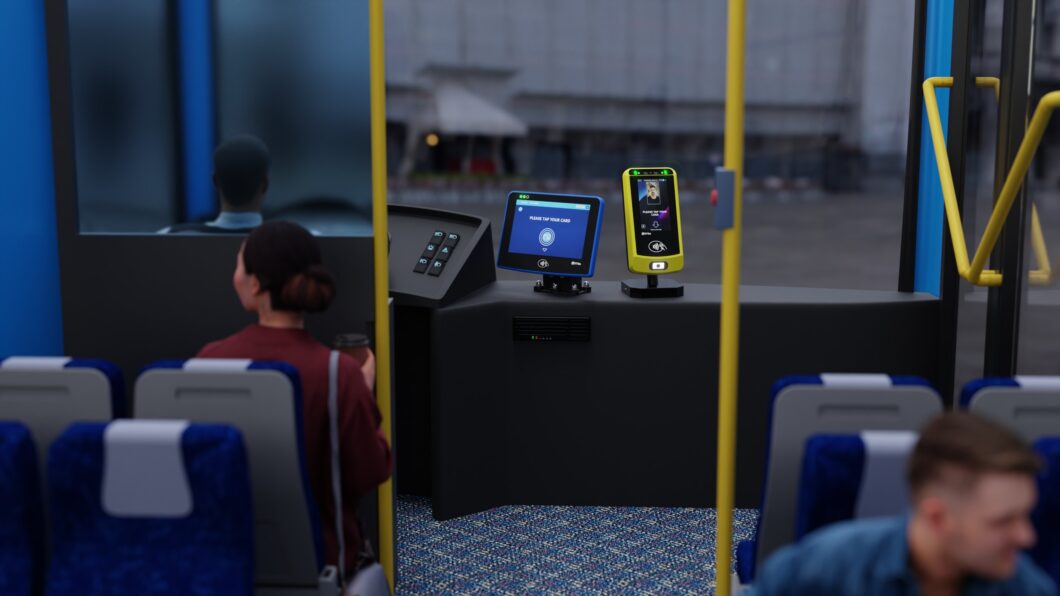
Convenience: Users can pay and validate tickets quickly using contactless cards or mobile devices, reducing the need for cash or physical tickets. Mobile and digital tickets that allows for the use of smartphones or digital wallets for purchasing and storing tickets, eliminating the need to carry physical tickets.
Faster Transactions: Automated systems speed up ticket issuance and validation, reducing queues and wait times at ticketing points.
Accessibility: Embedded systems often feature intuitive interfaces, such as touchscreens or voice commands, making them accessible to a wide range of users, including those with disabilities.
Real-Time Information: Users receive real-time updates about ticket status, fare changes, and system alerts, which improves their overall experience.
Key advantages for Operators:
Operational Efficiency: Reduces the need for manual ticket handling and fare collection, streamlining operations and lowering labor costs. Both, facilitates centralized control and monitoring of ticketing operations, allowing for easier management and coordination.
Enhanced Security: Embedded systems incorporate encryption and secure authentication methods, reducing the risk of ticket fraud and unauthorized access. Secure handling of sensitive data, such as payment information and personal details, ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
Data Collection and Analytics: Provides valuable data on passenger usage patterns, peak times, and transaction volumes, which can be used for better decision-making and operational improvements. Performance Monitoring: Allows for ongoing monitoring of system performance and maintenance needs, ensuring reliability and reducing downtime.
Scalability and Integration: Easily integrates with other systems, such as fare management or customer service platforms, and can be scaled to accommodate future needs or expansions. Allows for the addition of new features or updates without overhauling the entire system.
Cost Savings: Reduced Cash Handling: Minimizes the need for cash transactions and physical ticket production, lowering associated costs. Embedded systems often require less frequent maintenance compared to traditional systems, reducing long-term operational costs.