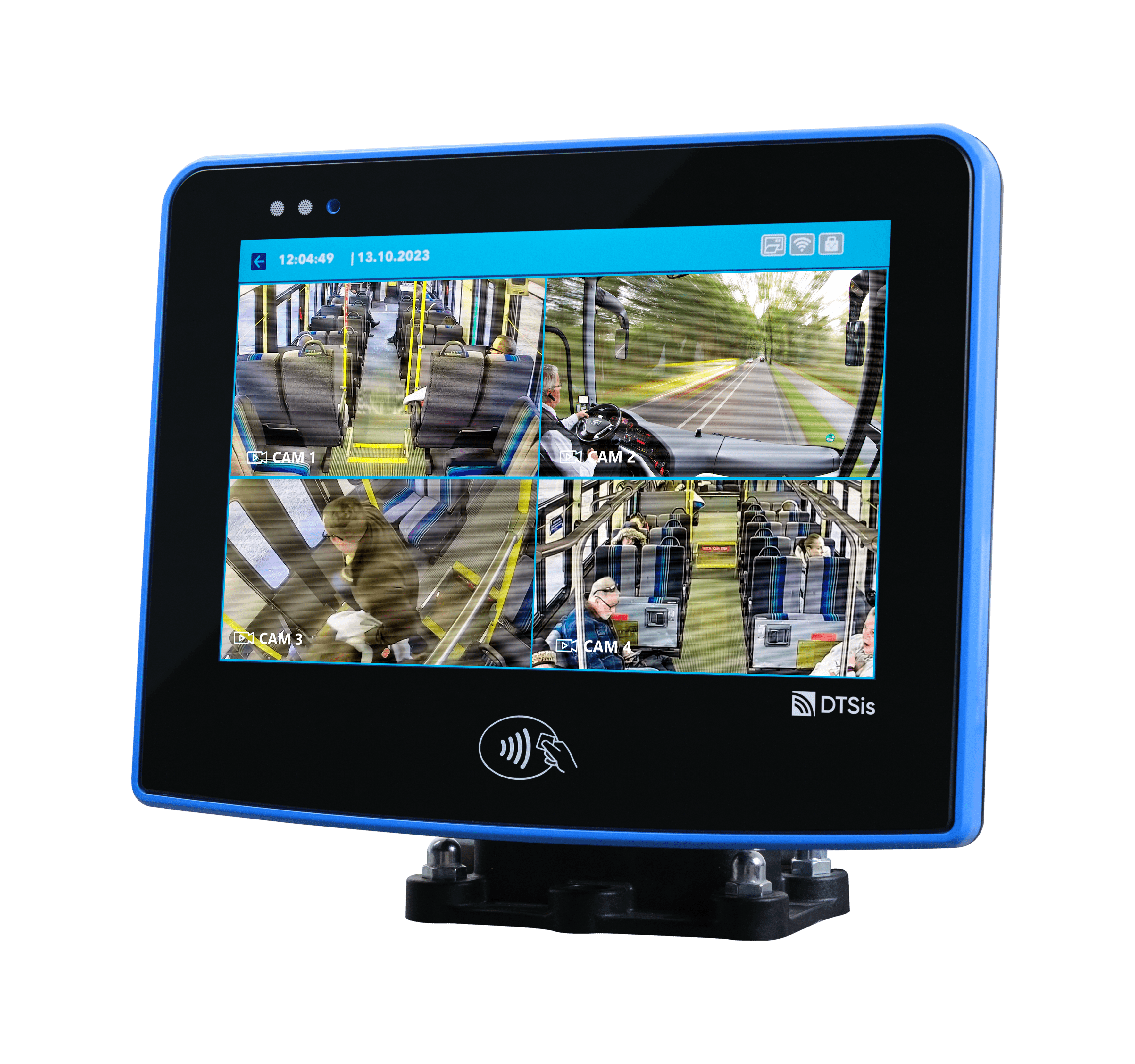
Contactless systems are becoming an essential part of everyday life across many sectors, including public transportation, access control, retail, and banking. This rapid adoption also brings an important responsibility: ensuring that these systems are reliable, durable, and long-lasting. These factors, which directly influence user experience, are closely linked to the technical precautions taken—especially during the manufacturing stage.
What Is ESD?
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) occurs when an electric current suddenly flows between two objects with different electrostatic potentials. This discharge can happen through direct contact or via an electrostatic field, and it can cause serious damage to sensitive electronic components.
In contactless systems such as NFC (Near Field Communication) and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), ESD represents a significant risk factor. Electrostatic discharges can lead to device malfunctions, performance degradation, or even complete system failure. For this reason, ESD protection plays a critical role in ensuring the reliability and continuity of contactless technologies.
Risks of ESD in Contactless Technologies
Without proper ESD protection, contactless systems may face the following issues:
Data errors: Communication between the card and the reader may be interrupted
Component damage: RFID/NFC electronic components may suffer permanent damage
Reduced product lifespan: Repeated ESD events accelerate component wear
Bu durumlar sistem güvenilirliğini ve kullanım sürekliliğini olumsuz etkiler.
Why Are Contactless Systems Sensitive to ESD?
Contactless systems rely on electronic circuits, antennas, and microcontrollers that enable wireless communication. These components are highly sensitive to sudden voltage spikes. The main sources of ESD risk include:
Human interaction: Static electricity can unintentionally build up when users bring cards, wearables, or devices close to readers
Environmental factors: Dry, low-humidity environments increase static charge accumulation and the likelihood of discharge
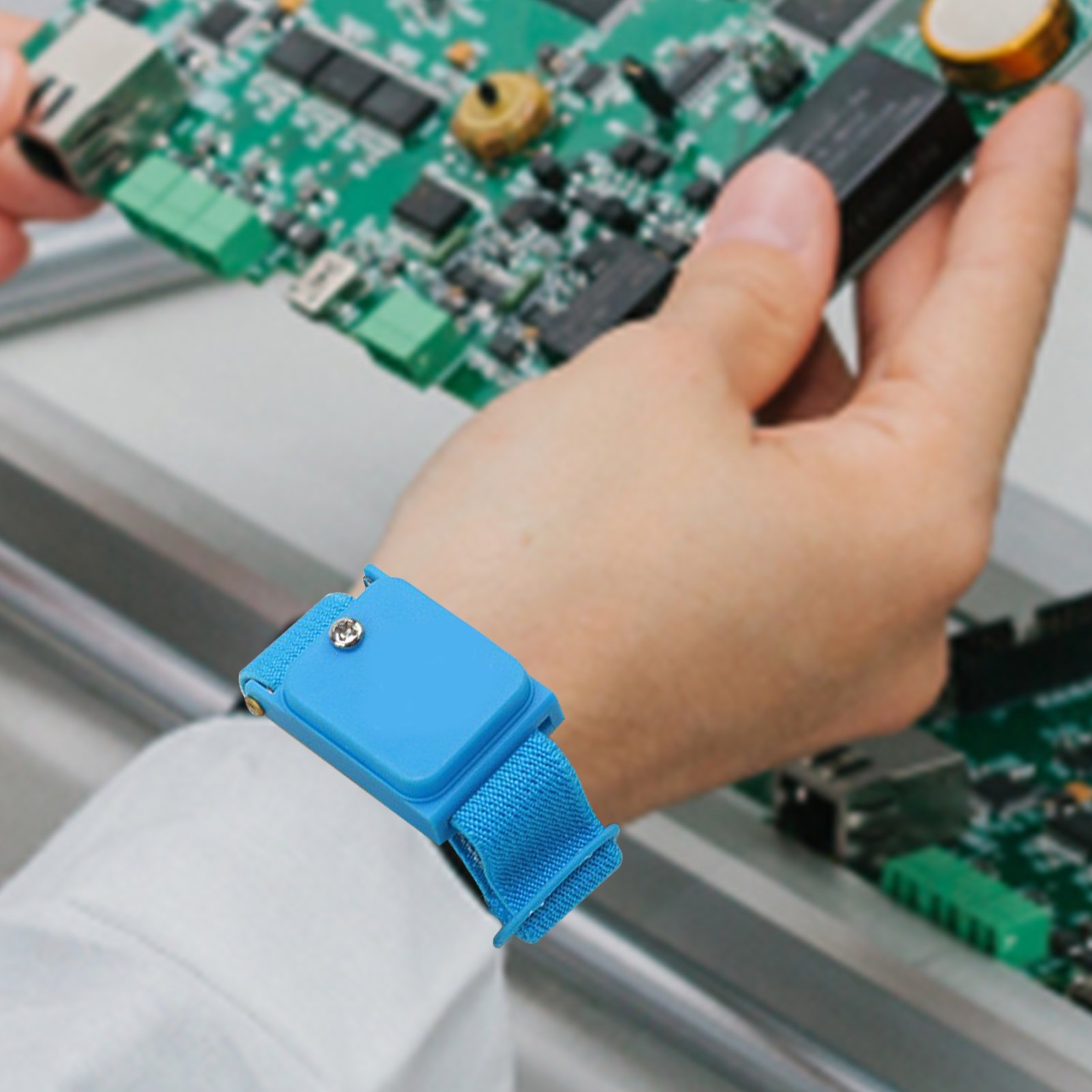
Manufacturing processes: Components may accumulate static energy during assembly, transportation, or packaging, which can be released in a damaging way