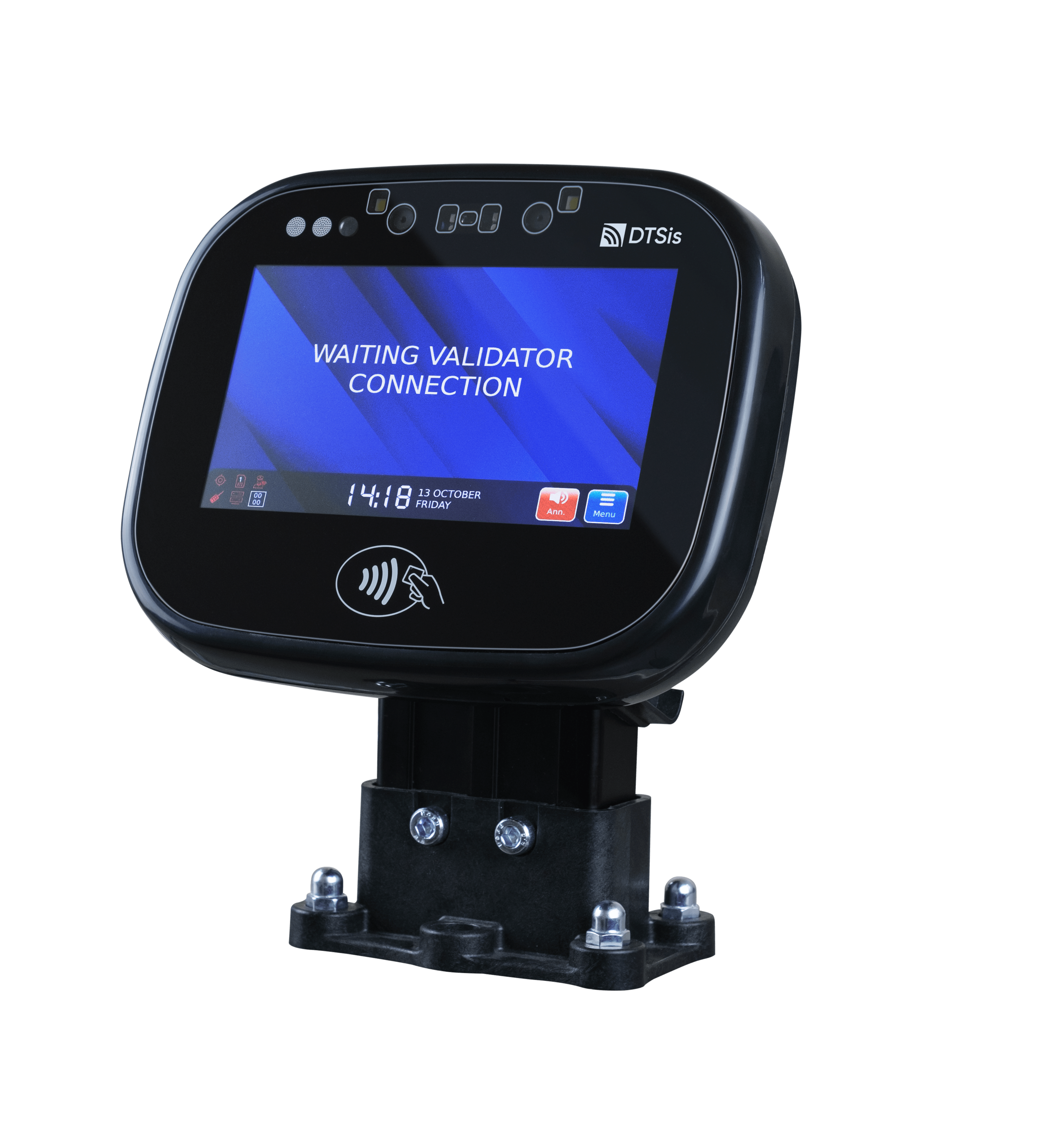
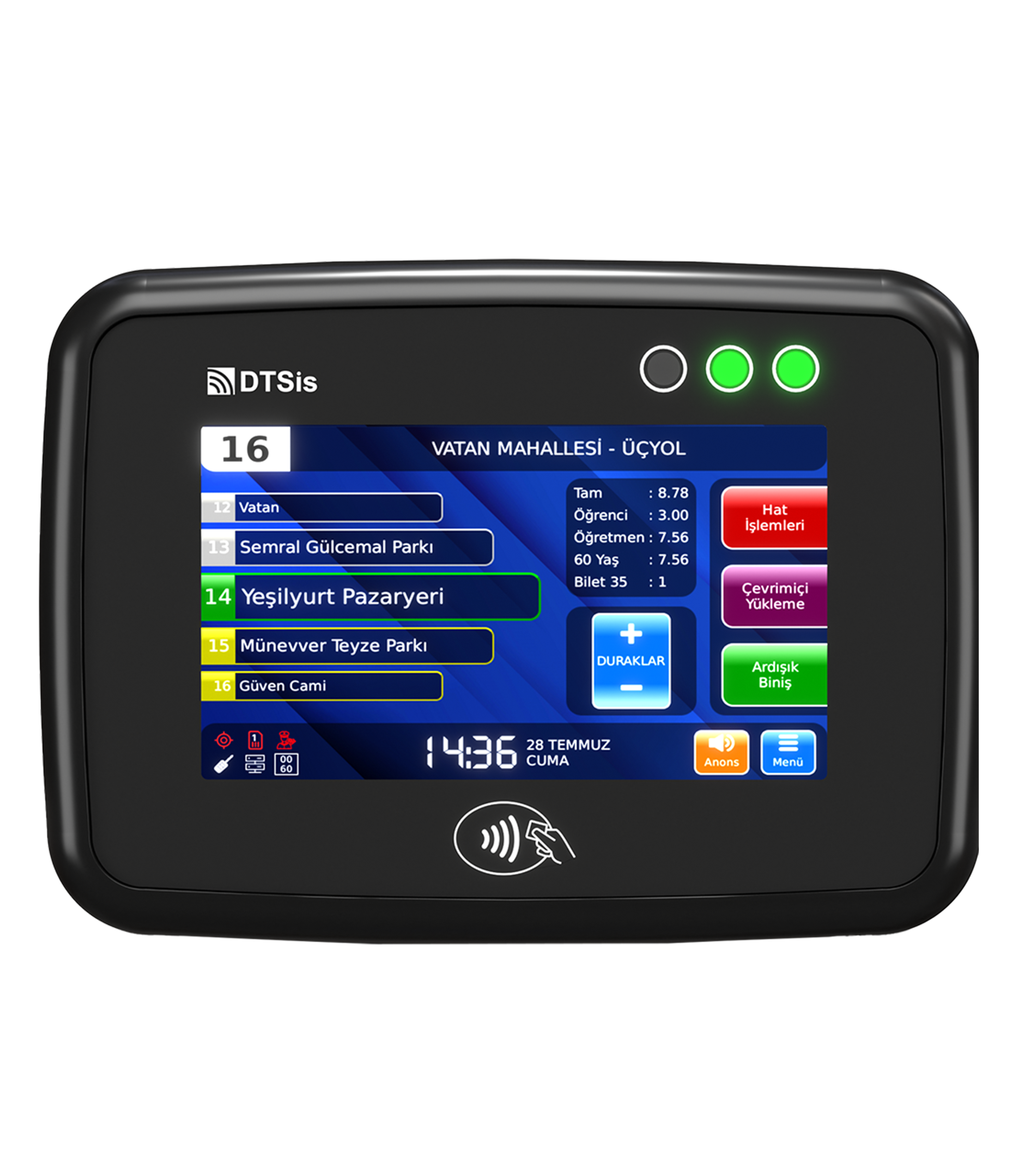
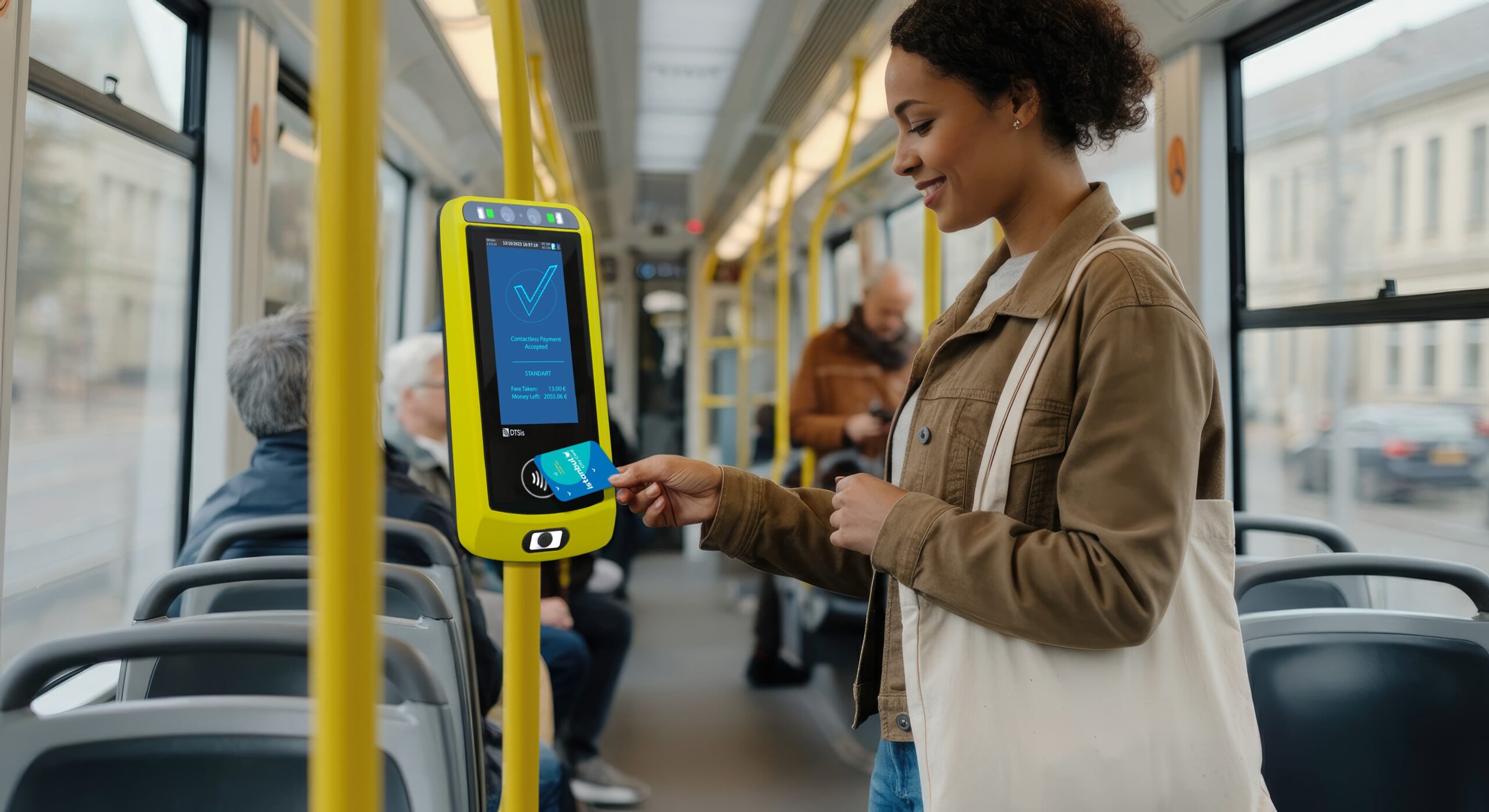
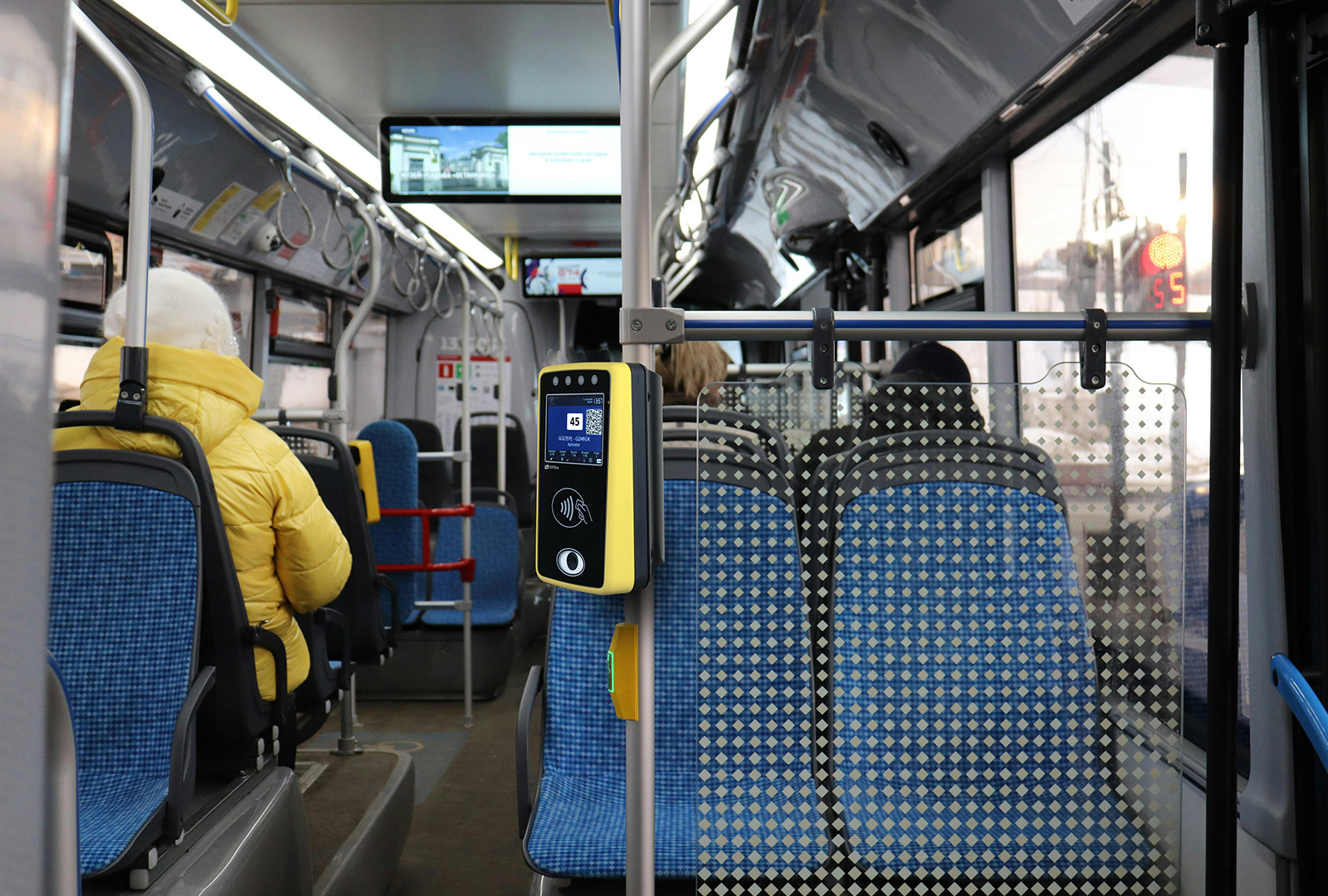
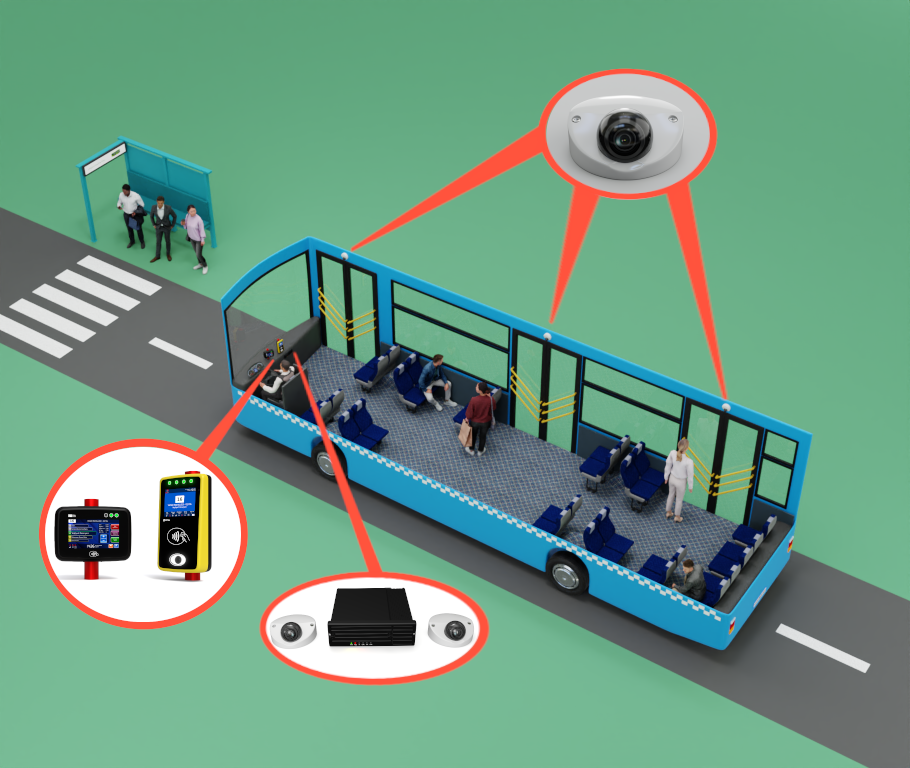
As public transportation systems evolve, security and convenience are becoming increasingly crucial for passengers and transit operators alike. One of the most promising advancements in this realm is the use of biometric data for passenger authentication. By leveraging unique biological identifiers such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans, transit systems can offer a more secure, efficient, and personalized travel experience. In this blog, we’ll explore how biometric data is transforming transit operations, the benefits it offers, and the future implications for urban mobility.
What is Biometric Authentication?
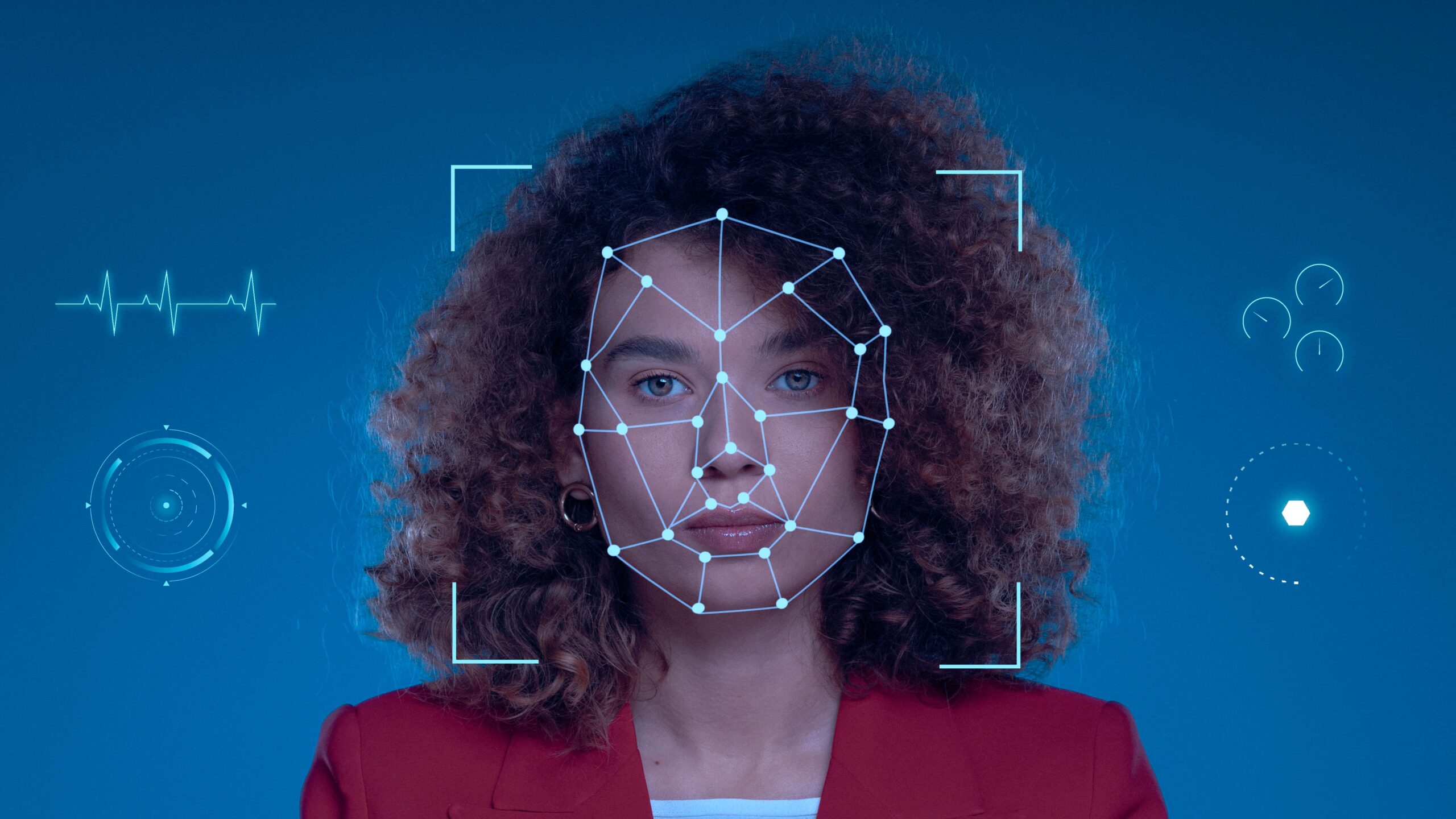
Biometric authentication uses physiological or behavioral characteristics to verify an individual’s identity. Unlike traditional methods such as passwords or ID cards, biometrics are inherently unique to each person, making them a robust and reliable form of identification. In the context of public transit, biometric systems are employed to authenticate passengers quickly and securely, streamlining access to services and improving overall system efficiency.
Key Biometric Technologies in Transit
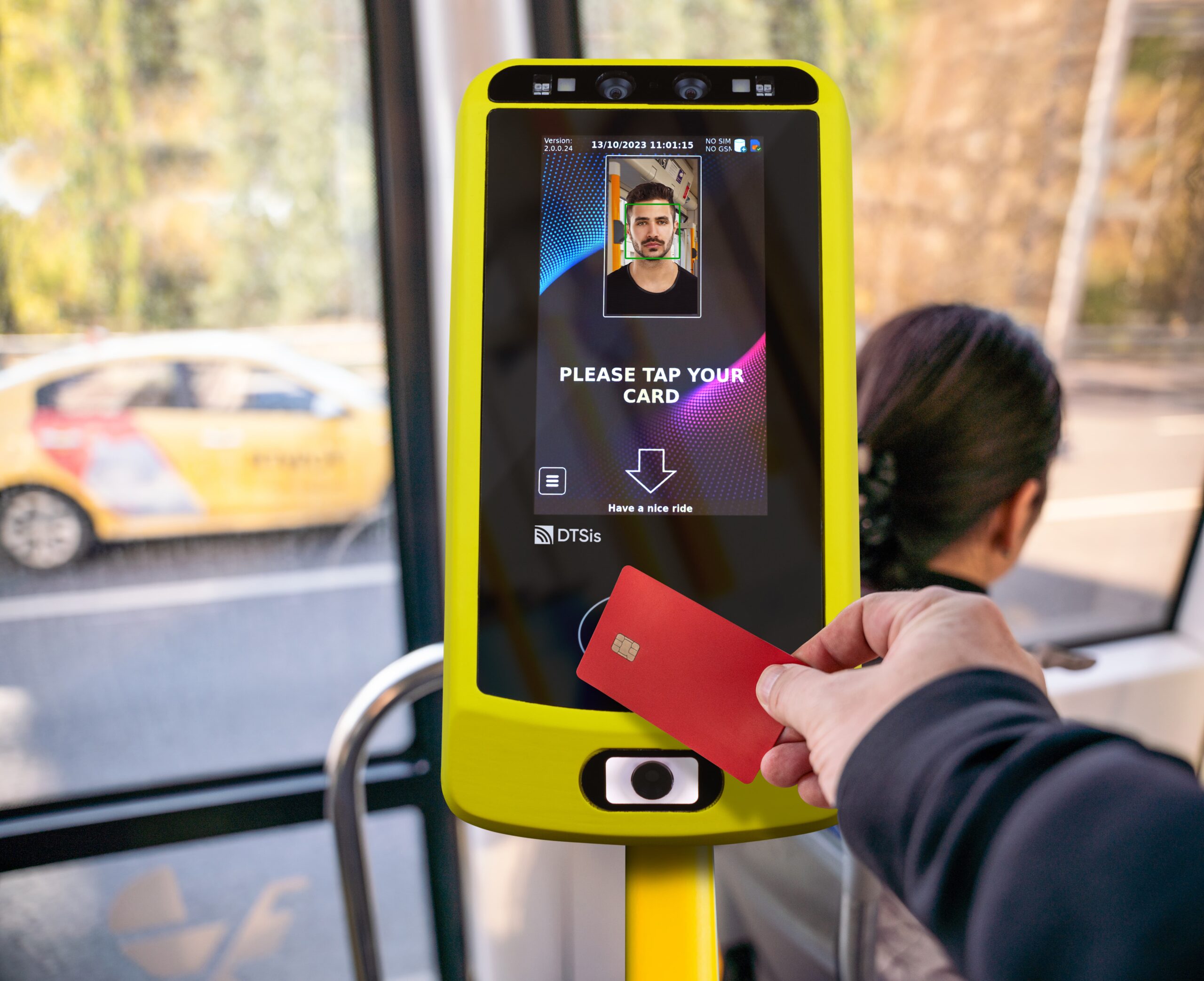
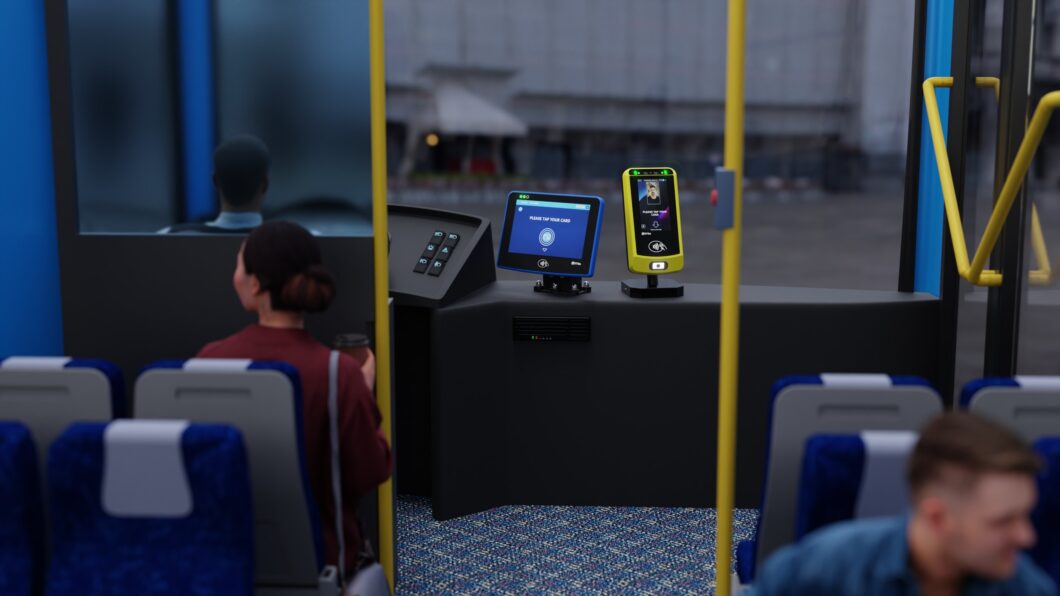
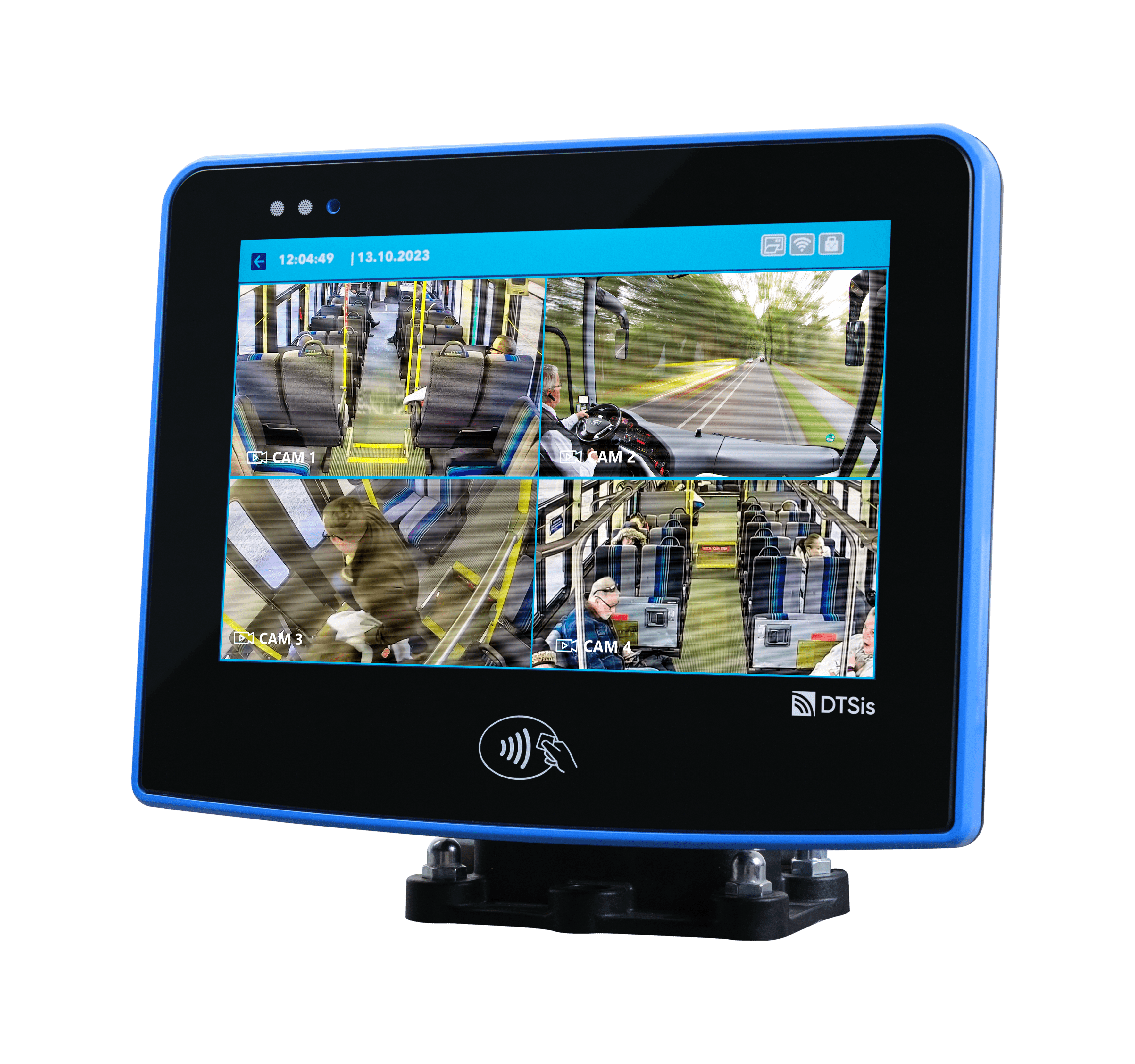
Facial Recognition: Facial recognition technology captures and analyzes unique facial features to verify identity. Cameras equipped with advanced algorithms scan passengers’ faces and match them against a database to grant or deny access. Facial recognition provides a contactless and non-intrusive method of authentication. It speeds up the boarding process, reduces the need for physical tickets, and enhances security by accurately identifying individuals.
Fingerprint Scanning: Fingerprint scanning involves capturing the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on a person’s fingers. This biometric data is compared to pre-registered fingerprints to verify identity.Fingerprint scanning is highly accurate and difficult to spoof. It provides a secure method of authentication and can be integrated into existing transit card systems or used independently.
Iris Recognition: Iris recognition technology analyzes the unique patterns in the colored part of the eye (the iris). This biometric identifier is highly distinct and difficult to replicate. Iris recognition offers one of the highest levels of security among biometric methods. It is suitable for high-security environments and can facilitate fast and accurate passenger authentication.
Benefits of Using Biometric Data in Transit
Enhanced Security: Biometric authentication significantly reduces the risk of fraudulent activities and unauthorized access. Unlike passwords or cards, biometric traits are difficult to duplicate or steal, providing a higher level of security for both passengers and transit operators.
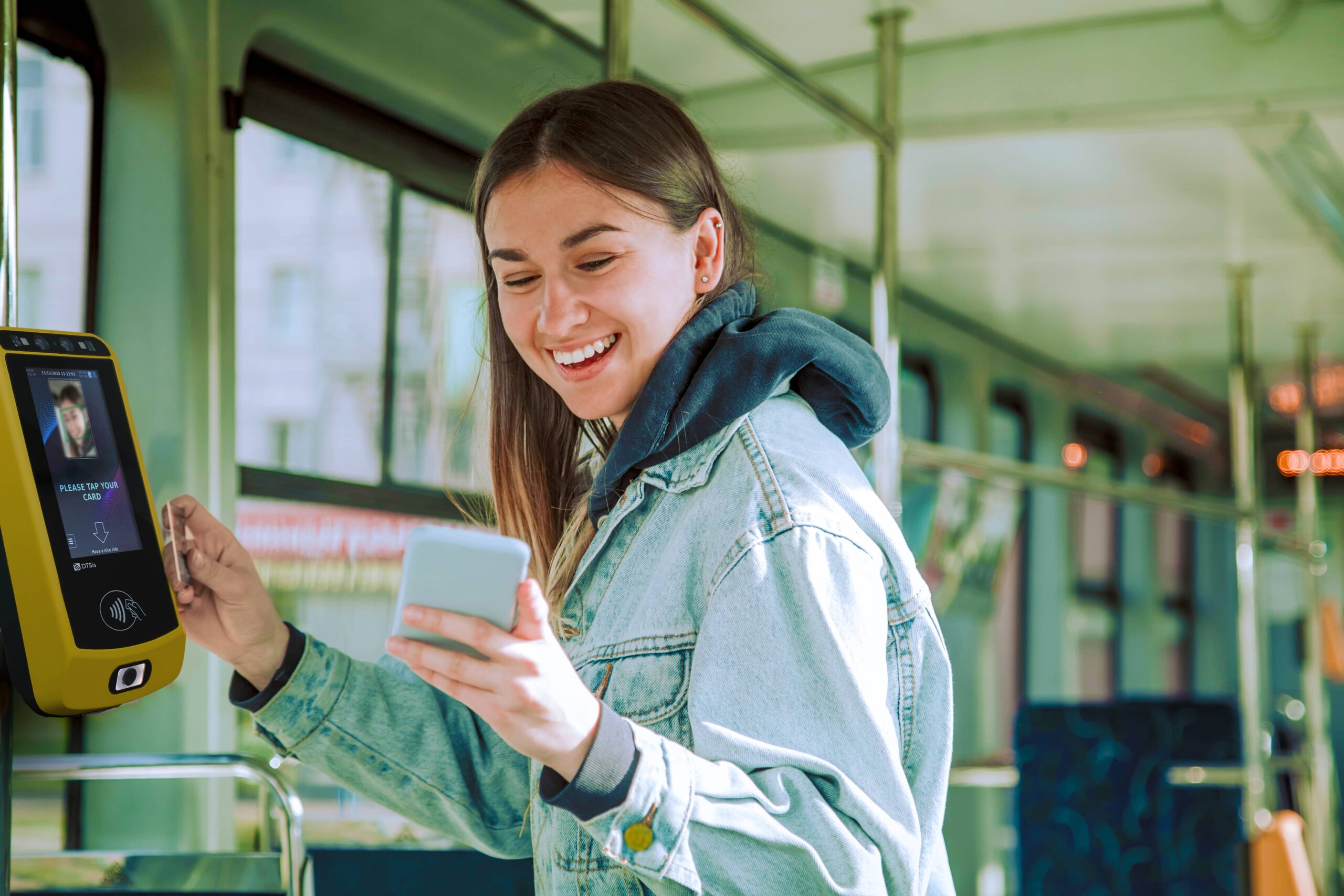
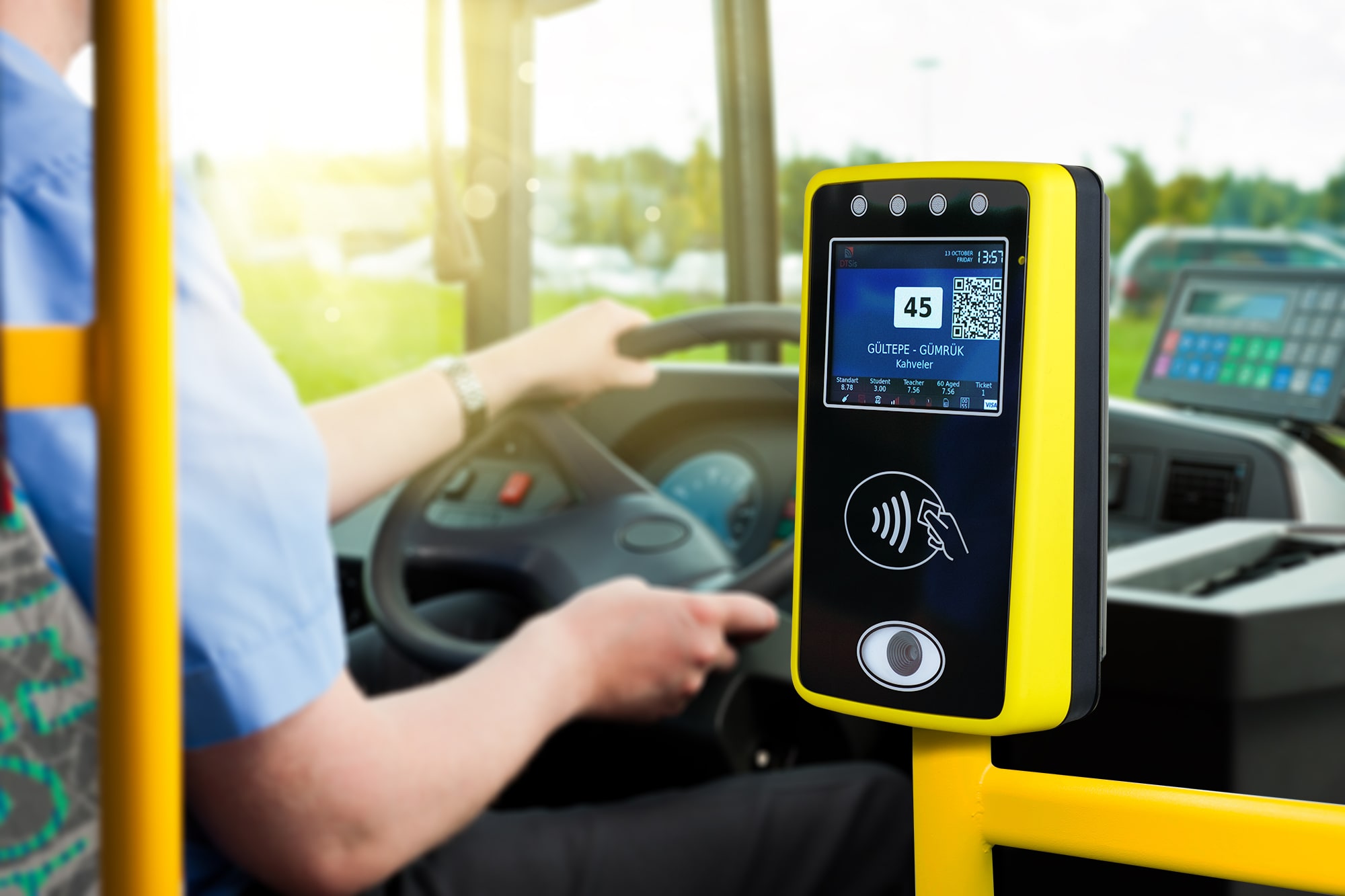
Streamlined Access: By eliminating the need for physical tickets or cards, biometric systems speed up the boarding process and reduce queues. Passengers can simply walk through biometric gates or scanners, making the transit experience more efficient and user-friendly.
Improved Passenger Experience: Biometric authentication offers a seamless and personalized travel experience. Passengers no longer need to carry physical tickets or remember passwords, and they can enjoy faster and more convenient access to transit services.
Operational Efficiency: Transit operators benefit from reduced administrative burdens and operational costs associated with managing physical tickets and cards. Biometric systems automate the authentication process and streamline fare collection, leading to more efficient operations.
Data-Driven Insights: The data collected through biometric systems can provide valuable insights into passenger behavior and usage patterns. Transit authorities can use this information to optimize services, improve scheduling, and enhance overall system performance.
Increased Accessibility: Biometric authentication can be particularly beneficial for passengers with disabilities. For example, voice recognition systems can provide an alternative to physical ticketing for those with mobility impairments.